Introduction:-
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, commonly referred to as Hodgkin’s disease, is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is a part of the immune system. The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland, and bone marrow, all of which play crucial roles in fighting infection. Unlike other types of lymphoma, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, which can be identified through biopsy. Though rare compared to other cancers, this disease is treatable, especially when caught early.
In this article, we’ll explore the various aspects of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, including what it is, early symptoms, stages, complications, treatment options, and preventive measures.
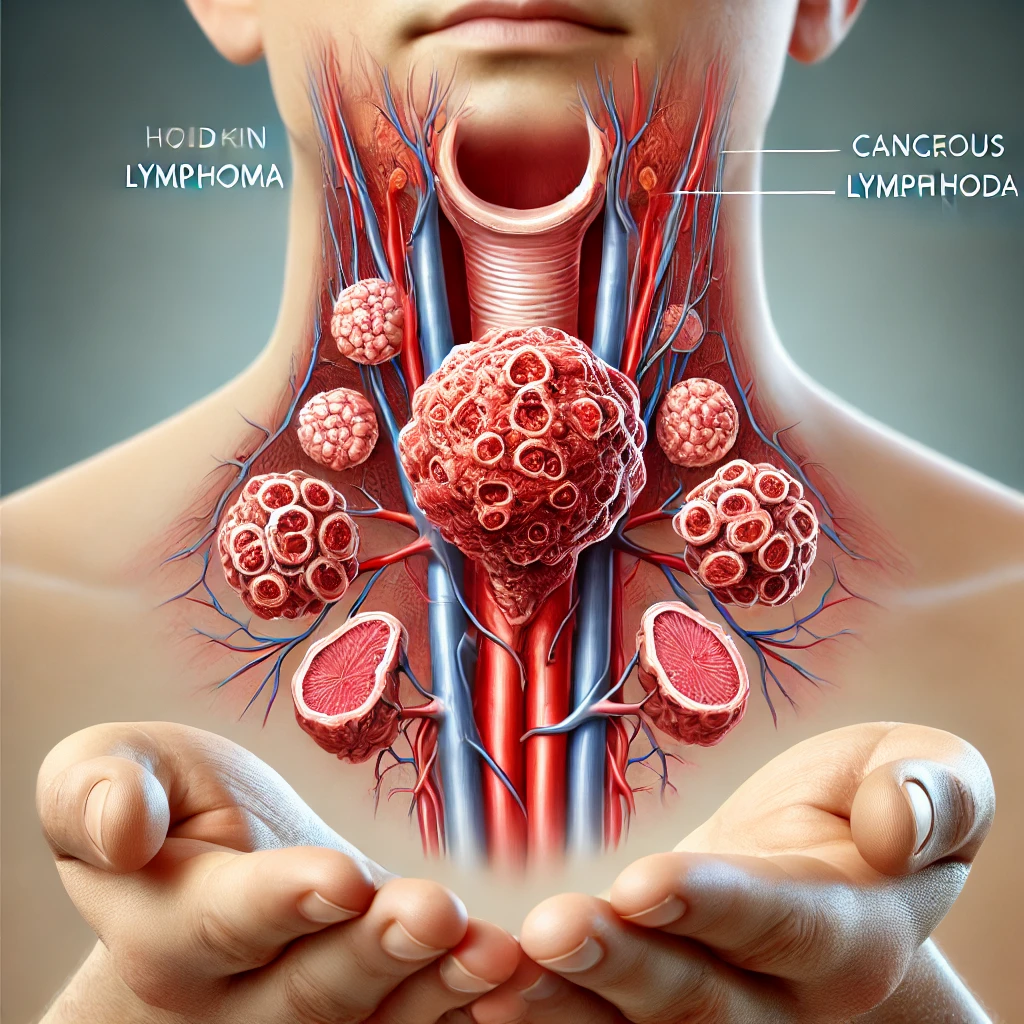
What is Hodgkin’s Lymphoma:-
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, specifically in white blood cells known as lymphocytes. These lymphocytes multiply abnormally and can spread beyond the lymphatic system. Over time, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma compromises the body’s ability to fight infections.
The distinguishing feature of this cancer is the presence of large, abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells, which can be seen under a microscope. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is further categorized into two main types: Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL) and Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma (NLPHL).
Early Symptoms:-
Recognizing the early symptoms of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma can significantly improve the prognosis. The most common symptoms include:
1. Swollen Lymph Nodes: The most noticeable early symptom is painless swelling of the lymph nodes in areas like the neck, armpits, or groin.
2. Fever and Night Sweats: Many patients experience unexplained fevers that come and go, often accompanied by excessive night sweats.
3. Fatigue: Persistent and unexplained fatigue is another hallmark of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
4. Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss, sometimes significant, can occur without changes in diet or exercise.
5. Itching: Itching all over the body, without any rash, is another less common symptom.
6. Chest Pain: If the lymph nodes in the chest area are affected, patients may experience shortness of breath, coughing, or chest pain.
7. Enlarged Spleen or Liver: Though less common, Hodgkin’s Lymphoma can cause swelling in these organs, which may be detected through imaging.
If you notice these symptoms, especially swollen lymph nodes that persist for more than two weeks, it’s essential to consult a doctor immediately.
Stages of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma:-
The progression of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is categorized into four main stages, depending on how far the cancer has spread. Early detection in the initial stages significantly increases the chances of successful treatment.
1. Stage 1: The cancer is localized to a single lymph node region or a single organ outside the lymphatic system.
2. Stage 2: The cancer is found in two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm or in one lymph node region and a nearby organ.
3. Stage 3: The cancer involves lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm, possibly including the spleen or an organ outside the lymphatic system.
4. Stage 4: This is the most advanced stage, where the cancer has spread beyond the lymph nodes to one or more organs, such as the liver, bone marrow, or lungs.
Challenges and Complications:-
As with most cancers, the challenges associated with Hodgkin’s Lymphoma are multi-faceted. Physically, the disease can cause a range of issues:
1. Weakened Immune System: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma attacks the lymphatic system, which plays a key role in immunity, leading to increased susceptibility to infections.
2. Organ Damage: When the cancer spreads to vital organs like the liver or lungs, it can severely impact their function.
3. Fatigue: Cancer treatments like chemotherapy can cause extreme fatigue, making it difficult for patients to carry out daily activities.
4. Fertility Issues: Chemotherapy and radiation can have long-term effects on fertility, especially in younger patients.
5. Secondary Cancers: Hodgkin’s Lymphoma patients are at a higher risk of developing secondary cancers, such as leukemia or breast cancer, as a result of treatment.
Treatment Options:-
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is one of the most treatable types of cancer, with a high cure rate, especially in early stages. The choice of treatment depends on the stage, the patient’s overall health, and other factors.
1. Chemotherapy: This is the most common treatment for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Chemotherapy uses powerful drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Depending on the stage, it may be the only treatment or be combined with radiation.
2. Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It is often used after chemotherapy to eliminate any remaining cancerous cells in a specific area.
3. Immunotherapy: For advanced stages or cases where the cancer returns, immunotherapy drugs like nivolumab or pembrolizumab may be used to boost the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
4. Stem Cell Transplant: For patients who don’t respond to initial treatments, a stem cell transplant may be an option. In this procedure, the patient receives healthy stem cells to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow.
5. Targeted Therapy: Unlike chemotherapy, which affects the whole body, targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth. Drugs like brentuximab vedotin are commonly used in targeted therapy for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction:-
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk:
1. Avoid Smoking: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of many types of cancer, including Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
2. Minimize Exposure to Pesticides and Chemicals: Long-term exposure to certain chemicals has been associated with a higher risk of lymphoma. Using protective equipment when handling hazardous substances can help mitigate this risk.
3. Regular Check-ups: Early detection is key to treating Hodgkin’s Lymphoma successfully. Regular health check-ups can help in spotting early signs of the disease.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and limiting alcohol intake can improve overall immunity and reduce cancer risks.
5. Manage Infections: Chronic infections like the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) have been linked to Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Treating these infections early may reduce risk.
READ MORE-Osteosarcoma
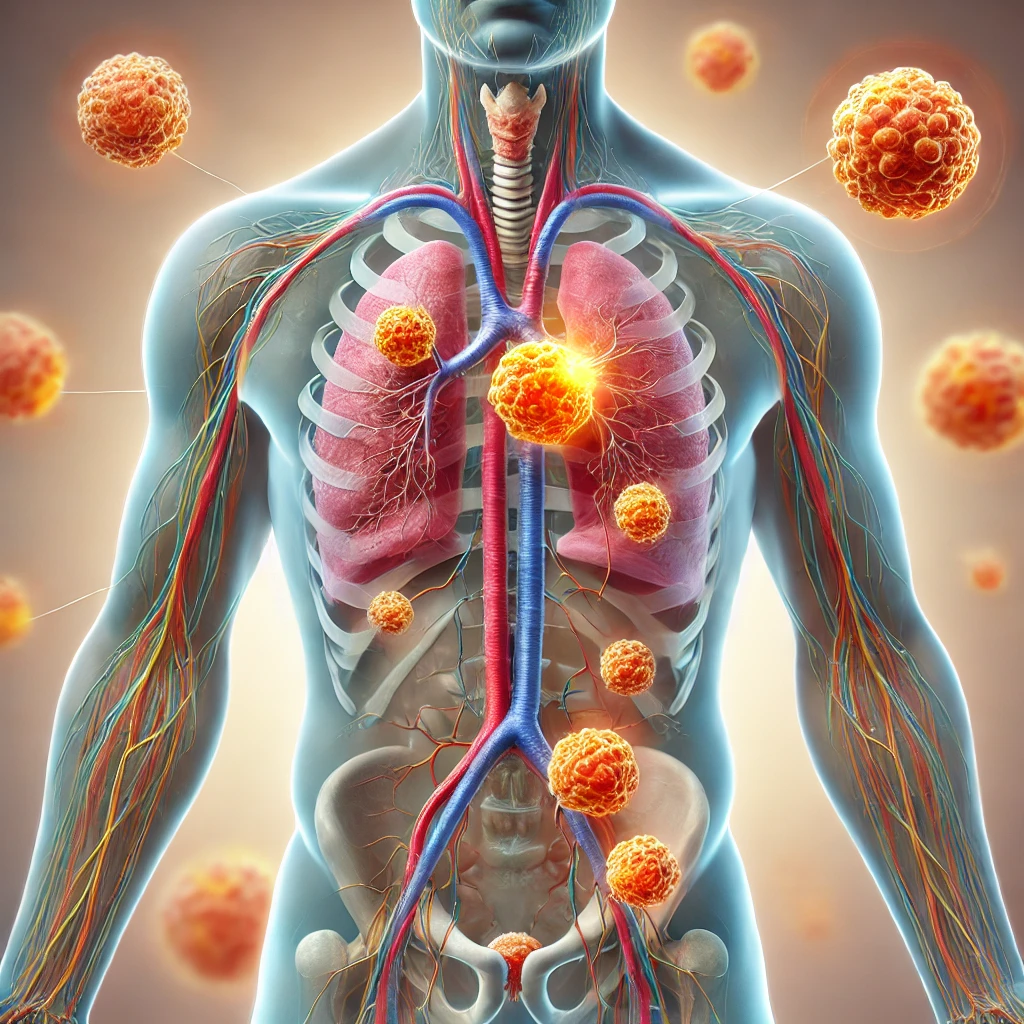
Conclusion:-
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a serious but highly treatable cancer, especially when caught in its early stages. Understanding the symptoms, stages, and treatment options empowers patients and their families to make informed decisions about their care. With advances in chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted treatments, the prognosis for Hodgkin’s Lymphoma continues to improve. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding known risk factors, and staying vigilant for early symptoms are critical in preventing and managing the disease.
For anyone experiencing any of the mentioned symptoms, especially swollen lymph nodes, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment make all the difference in the fight against Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
